Published on .
In the evolving landscape of Medicare Advantage (MA) plans, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) continually refine their Star Ratings to enhance patient safety and care quality. For the 2025 performance year, significant updates have been made concerning medication safety measures, particularly focusing on polypharmacy and the concurrent use of high-risk medications.
Updates on medication safety measures
CMS has officially integrated two critical measures from the Pharmacy Quality Alliance (PQA) measure set for the 2027 Star Ratings (measuring dates of service in 2025):
- Concurrent Use of Opioids and Benzodiazepines (COB): This measure evaluates the percentage of individuals aged 18 and older who have overlapping prescriptions of opioids and benzodiazepines for 30 or more cumulative days. The concurrent use of these medications can lead to severe respiratory depression and increased risk of fatal overdoses.
- Polypharmacy: Use of Multiple Anticholinergic Medications in Older Adults (Poly-ACH): This measure assesses the percentage of individuals aged 65 and older who are prescribed two or more unique anticholinergic medications concurrently for 30 or more cumulative days. Anticholinergics are associated with cognitive decline, increased risk of falls and other adverse effects in the elderly.
The third measure proposed in 2023, Polypharmacy: Use of Multiple Central Nervous System Active Medications in Older Adults (Poly-CNS), remains on the CMS display page for 2025. This measure monitors the percentage of older adults concurrently using three or more unique CNS-active medications, which can lead to heightened risks of falls, cognitive impairment and mortality.
Understanding the measures and their importance
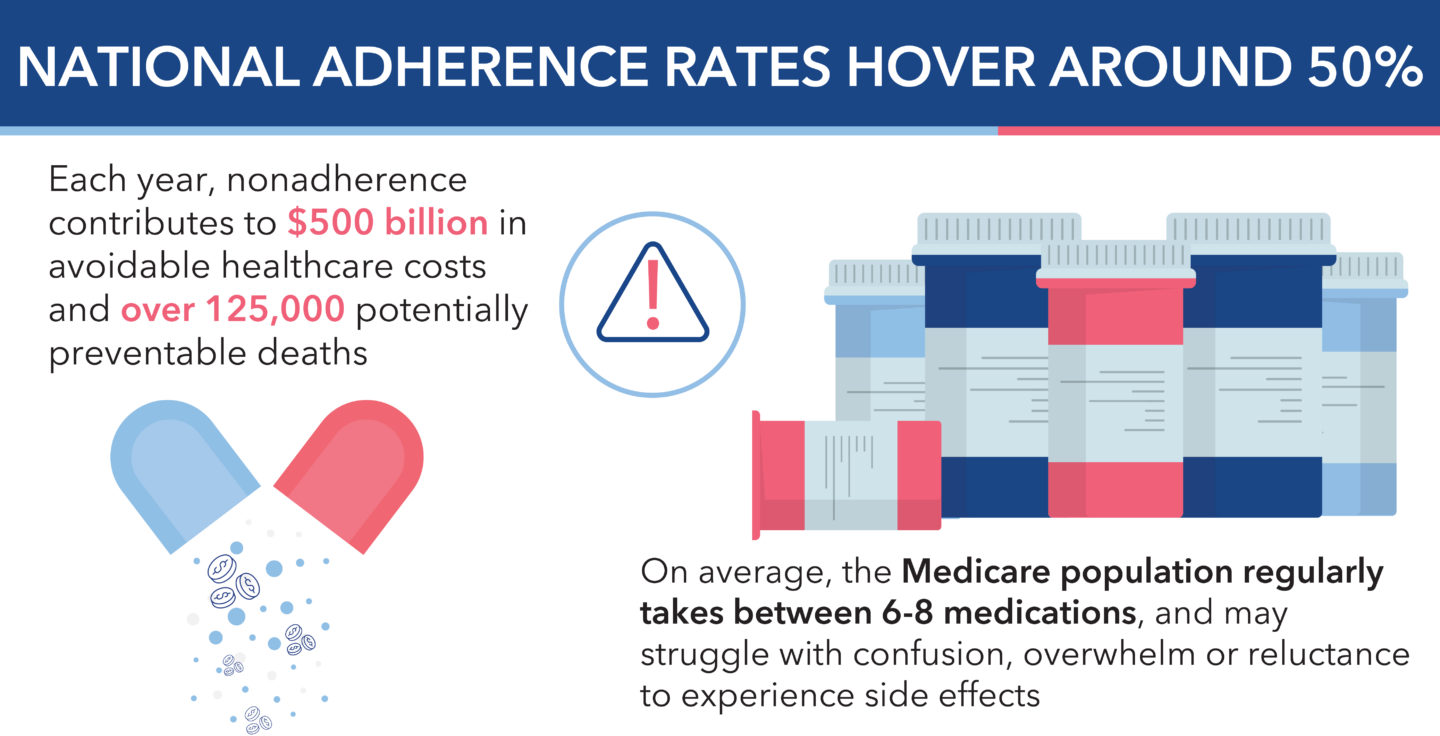
Polypharmacy, defined as the use of multiple medications by a patient, is common within Medicare populations due to the high prevalence of multiple chronic conditions that require treatment. While necessary in some cases, polypharmacy increases the risk of adverse drug events and drug interactions.
The opioid epidemic further complicates this issue. The misuse of opioids, often initially prescribed for chronic pain, has led to widespread addiction and overdose deaths. When combined with benzodiazepines, the risk of respiratory depression and fatal outcomes escalates significantly.
Anticholinergic medications, commonly prescribed for conditions like allergies, depression and urinary incontinence, can impair cognitive function and increase fall risk in older adults. Similarly, CNS-active medications, including antidepressants, antipsychotics and anticonvulsants, when used concurrently, can lead to sedation, confusion and impaired motor function.
CMS’s newly finalized measures, originally developed by PQA, emphasize the importance of medication safety. By moving these measures from display to Star Ratings, CMS underscores the critical need for health plans to support the management of high-risk prescriptions that frequently impact Medicare-eligible adults.
Strategies for MA plans to address these measures
Addressing medication safety measures requires a multifaceted approach:
- Sensitivity toward members. Plans need to be sensitive to the fact that members may feel they need these medications, making the topic particularly delicate. Members who have been on high-risk medications long-term may be resistant to change. Plans must ensure prescribers are equipped with strategies to have empathetic, informed discussions with their patients about transitioning to safer alternatives.
- Provider collaboration and support. Because of the sensitivity of this topic, it’s critical for plans to adopt a provider-first approach and work closely with prescribers to manage these high-risk medications. By proactively engaging with prescribers regarding members meeting measure criteria, plans can support clinical decision-making and de-prescribing efforts, including those needing dose titration. This process involves notifying providers when a member qualifies for a measure in order to prompt transitions to safer alternatives, when appropriate. Regular touchpoints between health plans and prescribers foster collaboration, ensuring that medication adjustments align with member health goals and risk mitigation.
- Omnichannel outreach. To successfully engage prescribers and alert them of member medication risk, plans should employ omnichannel outreach techniques, such as phone calls, EMR messaging and fax. Through this multi-layered approach, plans can reach prescribers by their preferred means, to fit organically within the practice workflow and maximize the possibility of successful connection—bolstering efforts toward safer medication regimens for members.
- Continuous monitoring. Plans should implement ongoing claims monitoring to track prescription patterns throughout the Stars performance year. This proactive approach ensures timely interventions when new high-risk medications are prescribed. Without daily surveillance analytics, plans and prescribers alike may be blinded to member medication fill patterns and potentially miss outreach opportunities for high-risk members. Ongoing claims tracking is essential for plans to maintain continuous oversight and adjust outreach efforts accordingly, to ensure longitudinal compliance.
As CMS continues to refine Star Ratings and places a stronger emphasis on medication safety, it is imperative for MA plans to proactively address these measures. Managing polypharmacy and high-risk medication use requires ongoing provider collaboration, continuous claims monitoring and proven engagement techniques to ensure safe prescribing practices. By taking a strategic and proactive approach, health plans can enhance member safety, reduce adverse drug events and drive better health outcomes.
Drive medication safety and manage risk
Supporting medication adherence and safety requires more than one-time interventions—it demands a strategic, data-driven and sustained approach. AdhereHealth specializes in helping health plans navigate these challenges with advanced technology, behavioral science–based engagement and personalized outreach. By partnering with AdhereHealth, MA plans can enhance their medication safety initiatives, ensuring better care for their members.
For more information about how AdhereHealth can support your Star Ratings strategy, contact us today!

Ryan Dacus, PharmD
Vice President, Product Development and Implementations